Classifications
For on-premise applications, companies manage all the underlying compute, storage, and networking infrastructure for their systems and services. Cloud computing can manage some or all of these aspects for their customers, depending on the type of service classification. There are three cloud computing service models, Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS). 1 2
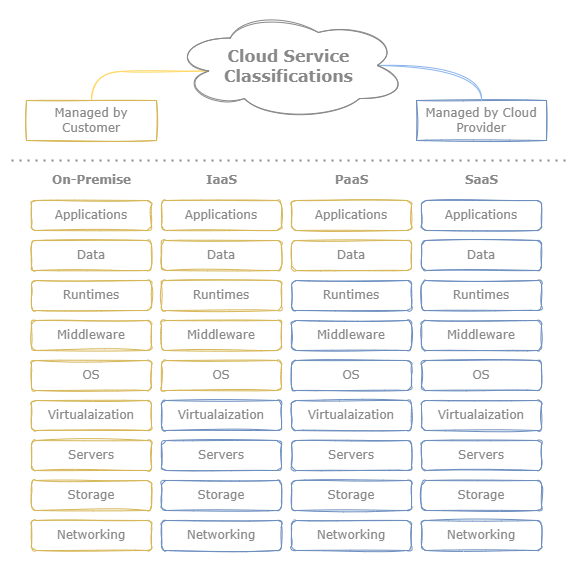
Figure 1: Cloud computing service classifications.
Infrastructure as a Service - IaaS
IaaS provides virtualized or physical servers for hosting applications. Cloud providers maintain the underlying network and hardware infrastructure while allowing cloud engineers control of the host OS and software. The hardware can be configured upon initially provisioning a new service, such as CPU, memory, storage, networking, GPU, etc. AWS EC2 service provides virtual servers known as instances for developers to host applications.
Platform as a Service - PaaS
PaaS manages all the components maintained by IaaS services in addition to host operating system and execution runtime, allowing users to primarily focus on application development. PaaS offerings typically manage infrastructure autoscaling, monitoring, and logging. Examples of PaaS would be Heroku, which allows developers to upload their applications to a server without having to worry about provisioning the underlying hardware or OS. The AWS offers a similar service known as Elastic Beanstalk.
A related offering would be Functions as a Service (FaaS), which, similar to PaaS services, allows for developers to deploy and execture code in the cloud. However, unlike PaaS, FaaS services tend to run in more restricted environments, such as limited CPU and memory configuration, execution time, application size, etc. while running in a more ephemeral environment.
Software as a Service - SaaS
For SaaS services, users manage none of the underlying infrastructure or application logic and are instead strictly service consumers. An example of this would be Dropbox or the AWS S3 service, where users can upload data through a web console or API while AWS maintains all backend storage.
-
NIST Definition of Cloud Computing: https://csrc.nist.gov/publications/detail/sp/800-145/final ↩︎
-
AWS Types of Cloud Computing: https://aws.amazon.com/types-of-cloud-computing/ ↩︎