Introduction
Definition
Cloud computing allows developers to provision and manage computational and network resources, such as servers, networks, or data stores, through a web interface, such as a web page or API. The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) formally defines cloud computing as follows:
Cloud computing is a model for enabling ubiquitous, convenient, on-demand network access to a shared pool of configurable computing resources (e.g., networks, servers, storage, applications, and services) that can be rapidly provisioned and released with minimal management effort or service provider interaction.
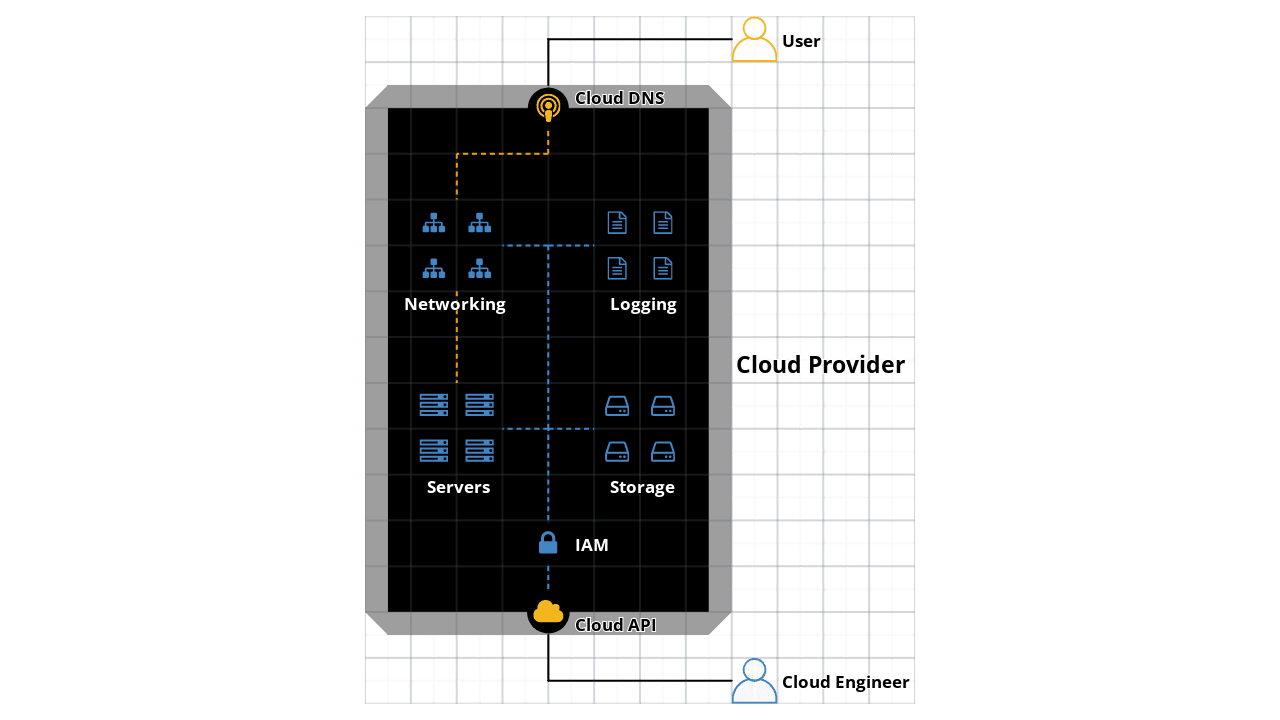
Companies and third-parties with cloud computing platform offerings are known as cloud providers. Popular cloud providers incude Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP).
Benefits
Cloud computing affords engineers numerous benefits when developing applications, such as:
- On-Demand: Servers, networks, and other cloud resources and be rapidly provisioned.
- Coss-Effectivness: Cloud providers operate at a scale beyond most organizations. As a result, customers are able to benefit from massive economies of scale when leveraging the cloud.
- Scalability: Organizations can horizontally and vertically scale infrastructure as needed.
Virtualization
To enable the on-demand provisioning, cloud providers heavily utilize virtualization to allocate and isolate computational resources and application processes amongst customers. It provides a layer of abstraction of the data center resource pool and can provide interfaces of storage, networking, and computation devices.
While cloud providers often use virtualization, certain use cases prohibit the use of shared CPU/Memory usage due to regulatory requirements. As such, cloud providers typically provide access to physical, non-virtualized hardware at additional costs.
Classifications
Cloud service offerings typically provide trade-offs between user configurability, costs, and overhead, ranging from fully user-configurable servers and virtual environments to completely managed services, such as for databases. Cloud services are broadly categorized as:
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS): Provides access to the underlying infrastructure.
- Platform as a Service (PaaS): Provides a runtime environment for easily deploying applications to the cloud.
- Software as a Service (SaaS): Software hosted in the cloud where end-users are not concerned with the underlying platform or infrastructure.
Cloud Native
The rise of cloud computing has accelerated the adoption of practices for developing robust cloud applications, collectively known as cloud-native development. These practices include microservices, containerization, and serverless development for improving application scalability, portability, deployability, and development speed.